The common etiology of all autoimmune disorders is chronic inflammation.
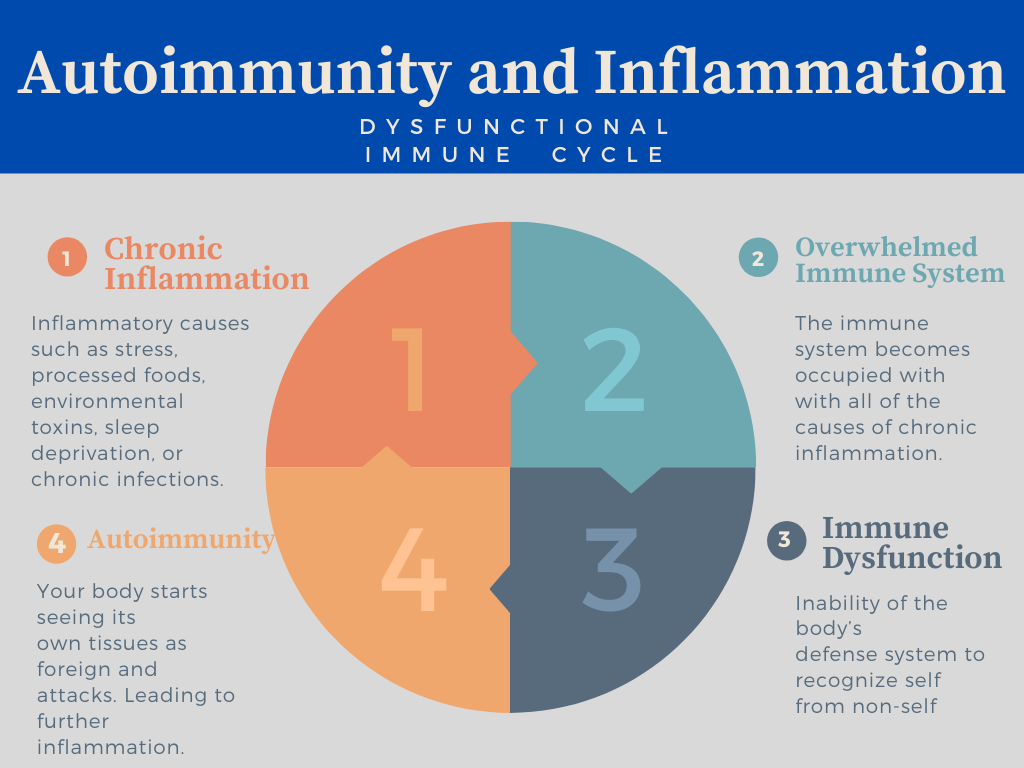
Chronic inflammation leads to an overwhelmed immune system, which leads to immune dysfunction and the inability of the body’s defense system to recognize self from non-self. This means your body starts seeing its own tissues as foreign and attacks the tissues like they are the common cold virus. This results in even more inflammation, and your body becomes stuck in a vicious dysfunctional cycle.
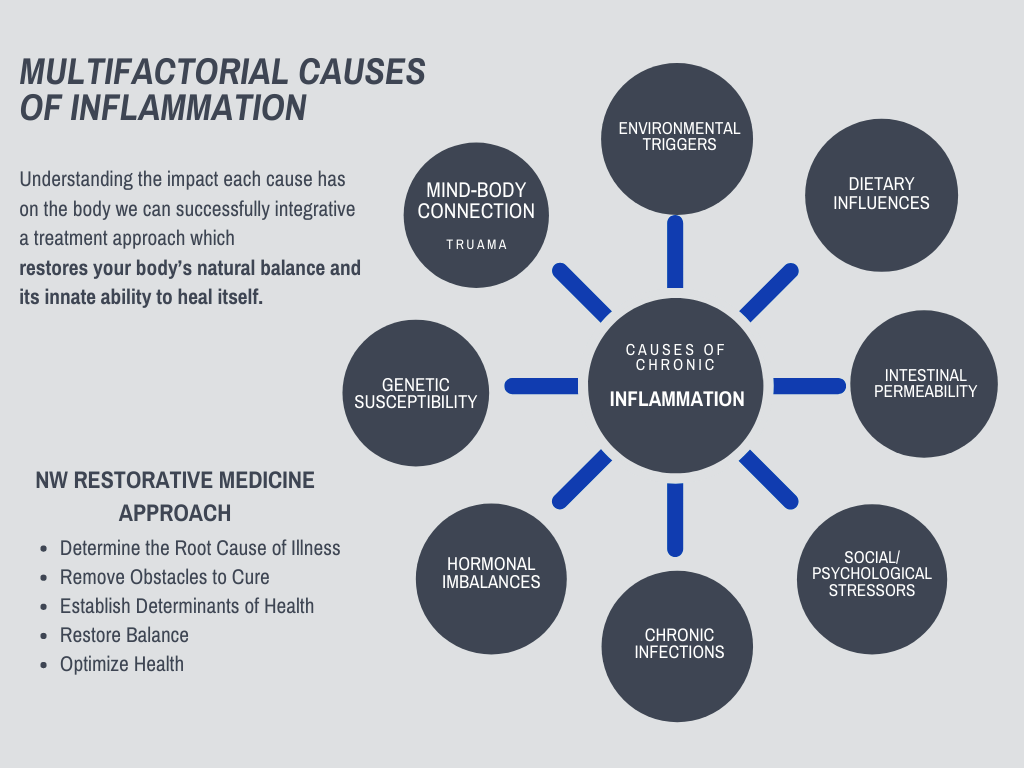
Environmental Exposure to and accumulation of heavy metals, pesticides, flame retardants, plasticizers, and solvents that we are exposed to through air, water, and food play a prevalent role in autoimmunity. These toxic chemicals and metals alter the body’s immune responses toward allergy and autoimmunity (attacking the body’s own tissues) and away from their natural role to act as surveillance against infections or foreign substances.
Dietary Influences play a huge role in autoimmunity because diet is a repetitive, daily occurrence. The pro-inflammatory effects of diet such as food allergies, food intolerances and nutrient deficiencies can shift the body towards chronic systemic inflammation putting an incredible strain on the body’s immune system.
Intestinal Permeability is often referred to as a “leaky gut”. This means there is some level of inflammation happening in the digestive tract.
Stress is the perception of a threat to physiological or psychological well-being. The body’s response to stress is to elevate pro-inflammatory protein messengers called cytokines. Chronic stress leads to chronic low-grade inflammation, which contributes to cellar dysfunction and immune dysregulation.
Chronic microbial Infections are common. These infections can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation, which results in an exhausted, overworked immune system. Microbial infections of viruses, bacteria, and parasites have tissue-damaging and disease-promoting effects. They incite an immune response which causes increased inflammation in the body. Chronic stimulation of the immune system can result in the body’s inability to differentiate self from non-self, contributing to cellular dysfunction and immune dysregulation.
Hormone Imbalances can promote or impede the genesis and perpetuation of inflammation and autoimmunity.
Genetic Susceptibility to autoimmunity is influenced by factors such as chromosomal mutations as well as epigenetic alterations. These altered patterns of genetic expression explain why one individual’s immune system starts attacking itself when exposed to environmental or food triggers and another individual’s immune system has more tolerance.
Mind-Body Connection especially post-trauma is extremely important for proper immune function. The autonomic nervous system has two main parts: the sympathetic (“fight or flight”) component and the parasympathetic (relaxation/rest & digest) component. The autonomic nervous system regulates metabolic homeostasis (balance) within the body by controlling heart rate, gastrointestinal motility, hormone, and neurotransmitter signaling as well as innate immune responses and inflammation during infection and tissue injury.


